Inheritance is one of the key features of OOP that allows us to create a new class from an existing class.
The new class that is created is known as subclass (child or derived class) and the existing class from where the child class is derived is known as superclass (parent or base class).
The extends keyword is used to perform inheritance in Java. For example,
class Animal {
// methods and fields
}
// use of extends keyword
// to perform inheritance
class Dog extends Animal {
// methods and fields of Animal
// methods and fields of Dog
}
In the above example, the Dog class is created by inheriting the methods and fields from the Animal class.
Here, Dog is the subclass and Animal is the superclass.
Example 1: Java Inheritance
class Animal {
// field and method of the parent class
String name;
public void eat() {
System.out.println("I can eat");
}
}
// inherit from Animal
class Dog extends Animal {
// new method in subclass
public void display() {
System.out.println("My name is " + name);
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an object of the subclass
Dog labrador = new Dog();
// access field of superclass
labrador.name = "Rohu";
labrador.display();
// call method of superclass
// using object of subclass
labrador.eat();
}
}
Output
My name is Rohu I can eat
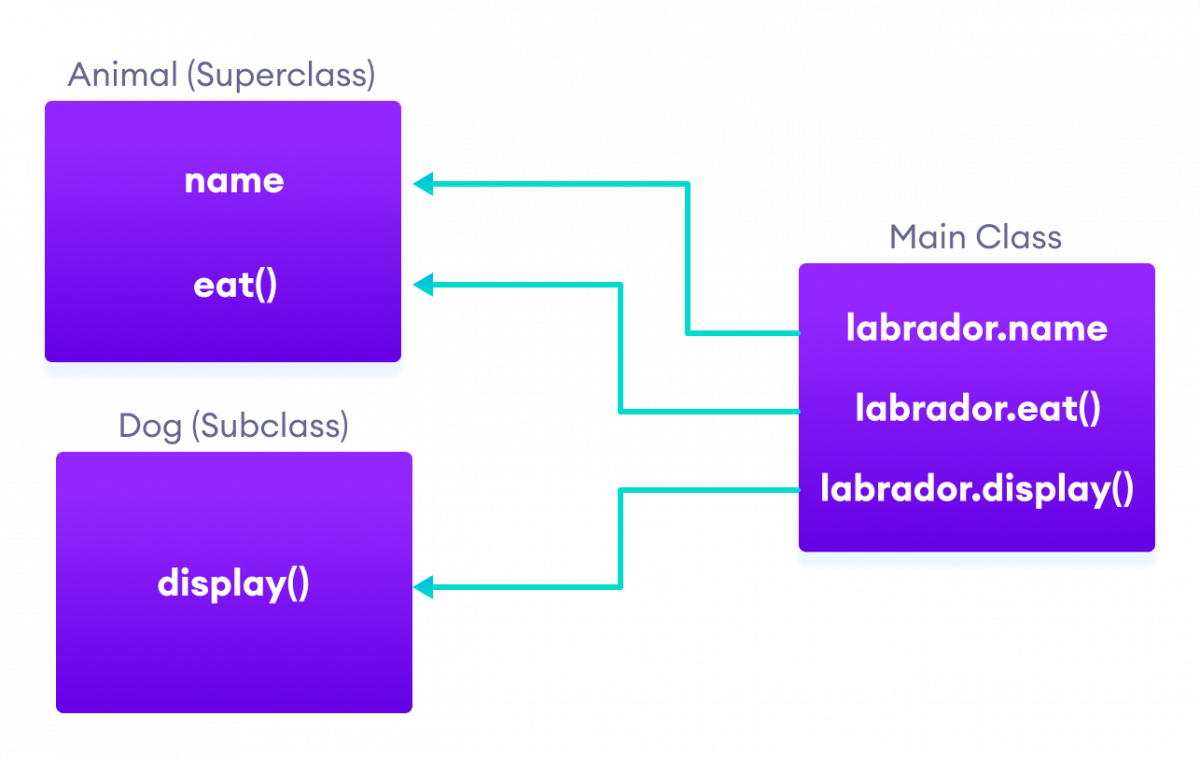
In the above example, we have derived a subclass Dog from superclass Animal. Notice the statements,
labrador.name = "Rohu";
labrador.eat();
Here, labrador is an object of Dog. However, name and eat() are the members of the Animal class.
Since Dog inherits the field and method from Animal, we are able to access the field and method using the object of the Dog.
is-a relationship
In Java, inheritance is an is-a relationship. That is, we use inheritance only if there exists an is-a relationship between two classes. For example,
- Car is a Vehicle
- Orange is a Fruit
- Surgeon is a Doctor
- Dog is an Animal
Here, Car can inherit from Vehicle, Orange can inherit from Fruit, and so on.
Method Overriding in Java Inheritance
In Example 1, we see the object of the subclass can access the method of the superclass.
However, if the same method is present in both the superclass and subclass, what will happen?
In this case, the method in the subclass overrides the method in the superclass. This concept is known as method overriding in Java.
Example 2: Method overriding in Java Inheritance
class Animal {
// method in the superclass
public void eat() {
System.out.println("I can eat");
}
}
// Dog inherits Animal
class Dog extends Animal {
// overriding the eat() method
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("I eat dog food");
}
// new method in subclass
public void bark() {
System.out.println("I can bark");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an object of the subclass
Dog labrador = new Dog();
// call the eat() method
labrador.eat();
labrador.bark();
}
}
Output
I eat dog food I can bark
In the above example, the eat() method is present in both the superclass Animal and the subclass Dog.
Here, we have created an object labrador of Dog.
Now when we call eat() using the object labrador, the method inside Dog is called. This is because the method inside the derived class overrides the method inside the base class.
This is called method overriding. To learn more, visit Java Method Overriding.
Note: We have used the @Override annotation to tell the compiler that we are overriding a method. However, the annotation is not mandatory. To learn more, visit Java Annotations.
super Keyword in Java Inheritance
Previously we saw that the same method in the subclass overrides the method in superclass.
In such a situation, the super keyword is used to call the method of the parent class from the method of the child class.
Example 3: super Keyword in Inheritance
class Animal {
// method in the superclass
public void eat() {
System.out.println("I can eat");
}
}
// Dog inherits Animal
class Dog extends Animal {
// overriding the eat() method
@Override
public void eat() {
// call method of superclass
super.eat();
System.out.println("I eat dog food");
}
// new method in subclass
public void bark() {
System.out.println("I can bark");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an object of the subclass
Dog labrador = new Dog();
// call the eat() method
labrador.eat();
labrador.bark();
}
}
Output
I can eat I eat dog food I can bark
In the above example, the eat() method is present in both the base class Animal and the derived class Dog. Notice the statement,
super.eat();
Here, the super keyword is used to call the eat() method present in the superclass.
We can also use the super keyword to call the constructor of the superclass from the constructor of the subclass. To learn more, visit Java super keyword.
protected Members in Inheritance
In Java, if a class includes protected fields and methods, then these fields and methods are accessible from the subclass of the class.
Example 4: protected Members in Inheritance
class Animal {
protected String name;
protected void display() {
System.out.println("I am an animal.");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public void getInfo() {
System.out.println("My name is " + name);
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an object of the subclass
Dog labrador = new Dog();
// access protected field and method
// using the object of subclass
labrador.name = "Rocky";
labrador.display();
labrador.getInfo();
}
}
Output
I am an animal. My name is Rocky
In the above example, we have created a class named Animal. The class includes a protected field: name and a method: display().
We have inherited the Dog class inherits Animal. Notice the statement,
labrador.name = "Rocky";
labrador.display();
Here, we are able to access the protected field and method of the superclass using the labrador object of the subclass.
Why use inheritance?
- The most important use of inheritance in Java is code reusability. The code that is present in the parent class can be directly used by the child class.
- Method overriding is also known as runtime polymorphism. Hence, we can achieve Polymorphism in Java with the help of inheritance.
Types of inheritance
There are five types of inheritance.
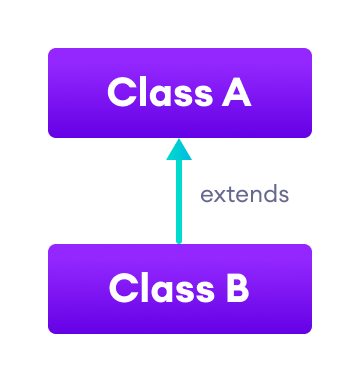
1. Single Inheritance
In single inheritance, a single subclass extends from a single superclass. For example,
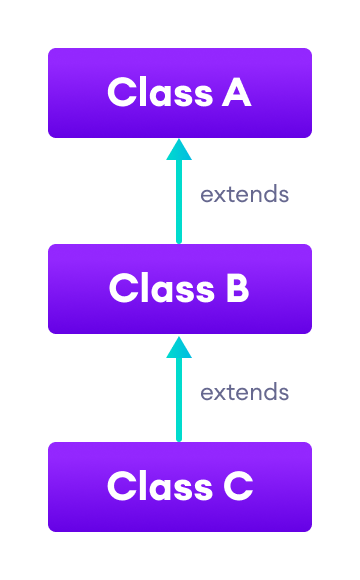
2. Multilevel Inheritance
In multilevel inheritance, a subclass extends from a superclass and then the same subclass acts as a superclass for another class. For example,
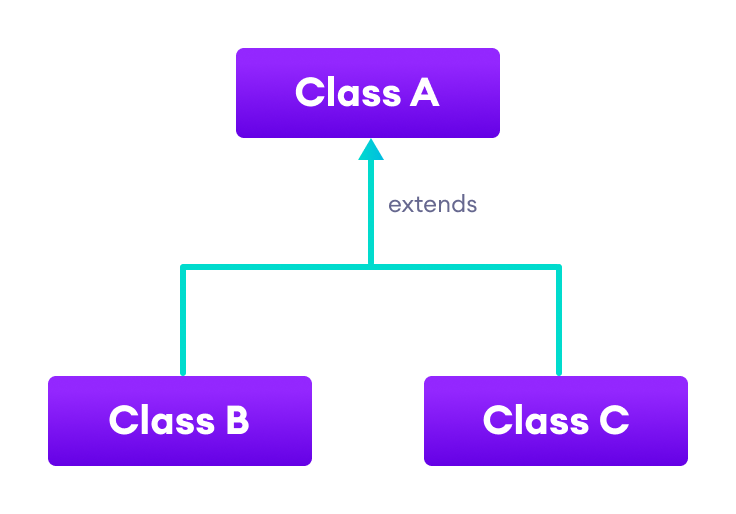
3. Hierarchical Inheritance
In hierarchical inheritance, multiple subclasses extend from a single superclass. For example,
4. Multiple Inheritance
In multiple inheritance, a single subclass extends from multiple superclasses. For example,
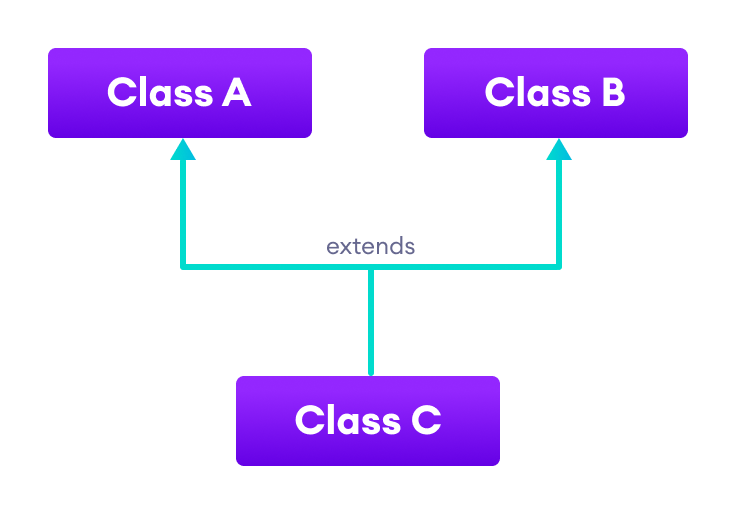
Note: Java doesn't support multiple inheritance. However, we can achieve multiple inheritance using interfaces. To learn more, visit Java implements multiple inheritance.
5. Hybrid Inheritance
Hybrid inheritance is a combination of two or more types of inheritance. For example,
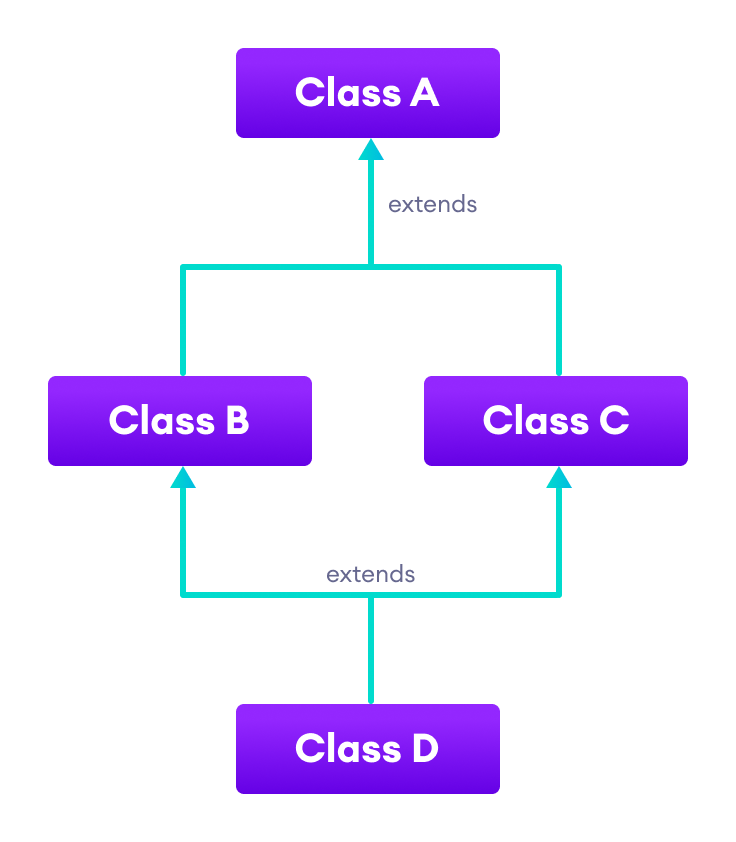
Here, we have combined hierarchical and multiple inheritance to form a hybrid inheritance.