Kotlin Default Argument
In Kotlin, you can provide default values to parameters in function definition.
If the function is called with arguments passed, those arguments are used as parameters. However, if the function is called without passing argument(s), default arguments are used.
How default arguments works?
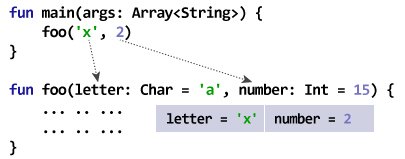
The function foo() takes two arguments. The arguments are provided with default values. However, foo() is called by passing both arguments in the above program. Hence, the default arguments are not used.
The value of letter and number will be 'x' and 2 respectively inside the foo() function.
Case II: All arguments are not passed

Here, only one (first) argument is passed to the foo() function. Hence, the first argument uses the value passed to the function. However, second argument number will take the default value since the second argument is not passed during function call.
The value of letter and number will be 'y' and 15 respectively inside the foo() function.
Case III: No argument is passed

Here, the foo() function is called without passing any argument. Hence, both arguments uses its default values.
The value of letter and number will be 'a' and 15 respectively inside the foo() function.
Example: Kotlin Default Argument
fun displayBorder(character: Char = '=', length: Int = 15) {
for (i in 1..length) {
print(character)
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
println("Output when no argument is passed:")
displayBorder()
println("\n\n'*' is used as a first argument.")
println("Output when first argument is passed:")
displayBorder('*')
println("\n\n'*' is used as a first argument.")
println("5 is used as a second argument.")
println("Output when both arguments are passed:")
displayBorder('*', 5)
}
When you run the program, the output will be:
Output when no argument is passed: =============== '*' is used as a first argument. Output when first argument is passed: *************** '*' is used as a first argument. 5 is used as a second argument. Output when both arguments are passed: *****
Kotlin named argument
Before talking about named argument, let us consider a little modification of the above code:
fun displayBorder(character: Char = '=', length: Int = 15) {
for (i in 1..length) {
print(character)
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
displayBorder(5)
}
Here, we are trying to pass second argument to the displayBorder() function, and use default argument for first argument. However, this code will give use an error. It's because the compiler thinks we are trying to provide 5 (Int value) to character (Char type).
To solve this situation, named arguments can be used. Here' how:
Example: Kotlin named argument
fun displayBorder(character: Char = '=', length: Int = 15) {
for (i in 1..length) {
print(character)
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
displayBorder(length = 5)
}
When you run the program, the output will be:
=====
In the above program, we are using named argument (length = 5) specifying that the length parameter in the function definition should take this value (doesn't matter the position of the argument).

The first argument character uses the default value '=' in the program.