In C++ programming, we can pass objects to a function in a similar manner as passing regular arguments.
Example 1: C++ Pass Objects to Function
// C++ program to calculate the average marks of two students
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Student {
public:
double marks;
// constructor to initialize marks
Student(double m) {
marks = m;
}
};
// function that has objects as parameters
void calculateAverage(Student s1, Student s2) {
// calculate the average of marks of s1 and s2
double average = (s1.marks + s2.marks) / 2;
cout << "Average Marks = " << average << endl;
}
int main() {
Student student1(88.0), student2(56.0);
// pass the objects as arguments
calculateAverage(student1, student2);
return 0;
}
Output
Average Marks = 72
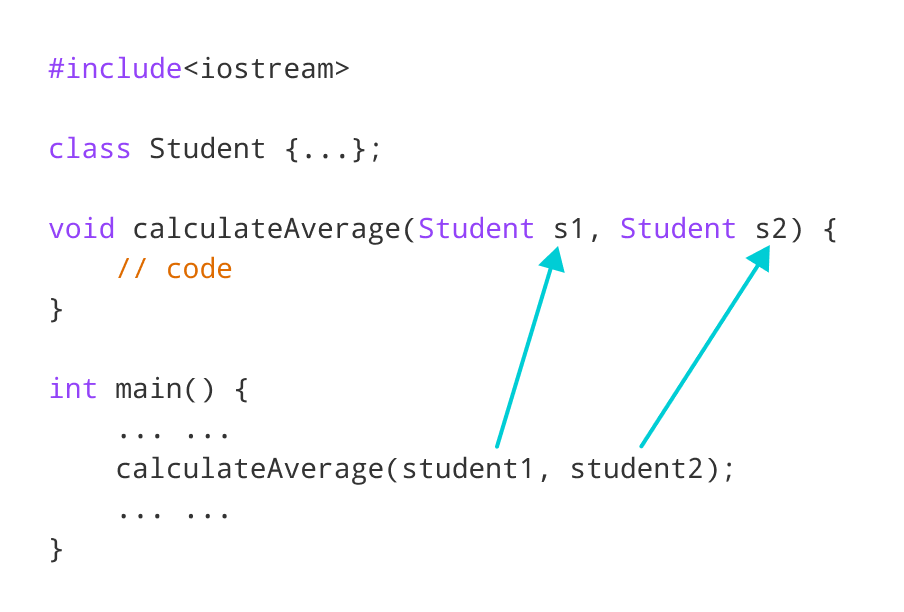
Here, we have passed two Student objects student1 and student2 as arguments to the calculateAverage() function.
Example 2: C++ Return Object from a Function
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Student {
public:
double marks1, marks2;
};
// function that returns object of Student
Student createStudent() {
Student student;
// Initialize member variables of Student
student.marks1 = 96.5;
student.marks2 = 75.0;
// print member variables of Student
cout << "Marks 1 = " << student.marks1 << endl;
cout << "Marks 2 = " << student.marks2 << endl;
return student;
}
int main() {
Student student1;
// Call function
student1 = createStudent();
return 0;
}
Output
Marks1 = 96.5 Marks2 = 75
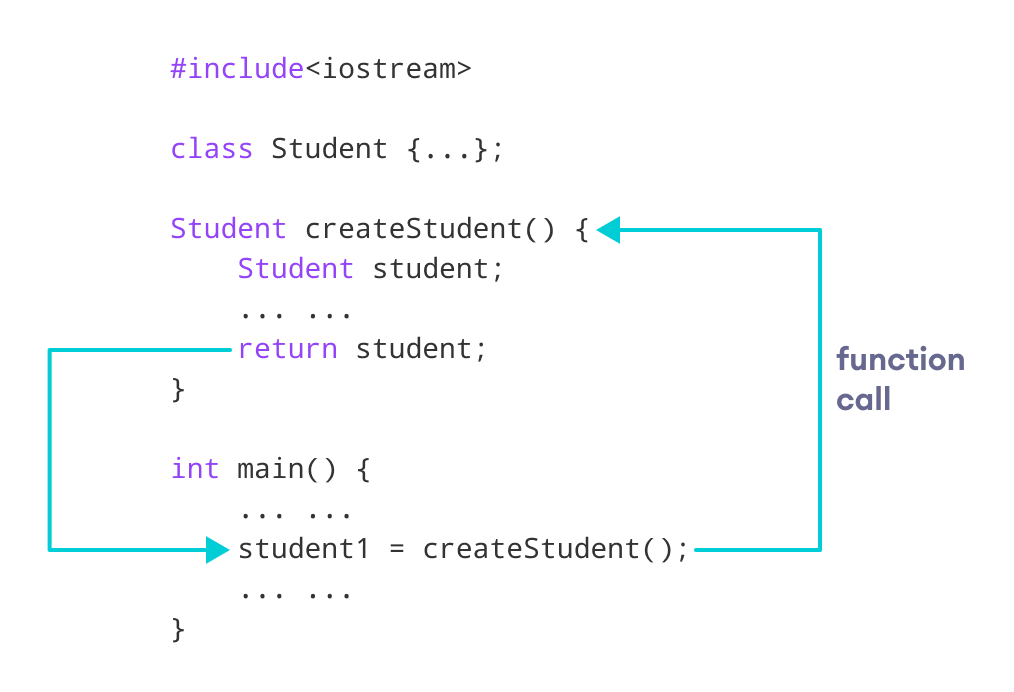
In this program, we have created a function createStudent() that returns an object of Student class.
We have called createStudent() from the main() method.
// Call function
student1 = createStudent();
Here, we are storing the object returned by the createStudent() method in the student1.